Understanding DDoS Attacks: What You Need to Know
In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses and individuals rely heavily on the internet for communication, transactions, and day-to-day operations. However, with this increased dependency comes a growing risk of cyber threats. One of the most common and disruptive types of cyberattacks is the DDoS attack. So, what exactly is it—and why should you care?
What Is a DDoS Attack?
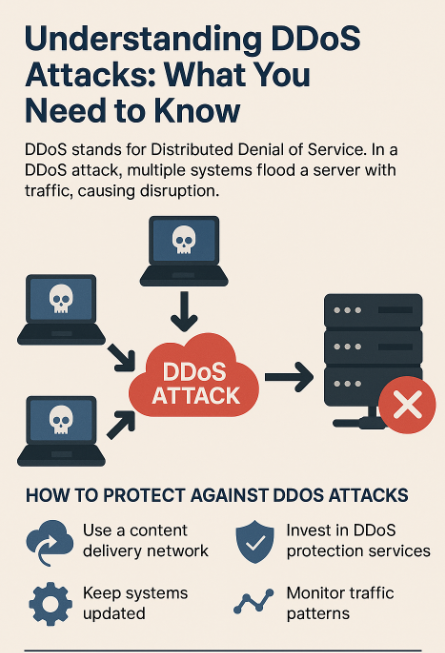
DDoS, which stands for Distributed Denial of Service, is a cyberattack that aims to shut down a website, server, or network by overwhelming it with traffic. Instead of a single source, the attack comes from multiple systems simultaneously, making it harder to stop. As a result, the system slows down significantly or becomes completely inaccessible.
To visualize it, imagine a highway that can handle a thousand cars per hour. Suddenly, ten thousand cars try to get on at once. The road clogs up, and no one gets through. That’s exactly what happens to a server during a DDoS attack.
How Does It Work?
DDoS attacks usually rely on a botnet, which is a network of malware-infected devices such as computers, smartphones, and even smart home appliances. Cybercriminals take control of these devices without the owners’ knowledge. Then, they use them to flood a target with fake requests.
Consequently, the server becomes too busy dealing with fake traffic to respond to real users. In many cases, the attack can last for hours or even days, causing serious disruption.
Common Types of DDoS Attacks
To better understand the threat, let’s break down the most common forms of DDoS attacks:
- Volume-Based Attacks: These aim to saturate the bandwidth by sending massive amounts of traffic.
- Protocol Attacks: These target weaknesses in network protocols, exhausting server resources.
- Application Layer Attacks: These focus on specific web applications, like login pages, trying to crash them with repeated requests.
Why Are DDoS Attacks Dangerous?
The dangers of DDoS attacks go far beyond inconvenience. Here are a few critical reasons why they’re so serious:
- They disrupt business operations: When a website goes down, customers can’t access products or services, resulting in lost sales.
- They damage reputation: Frequent downtime can lead to a loss of trust among customers and partners.
- They serve as distractions: While teams are focused on stopping the DDoS, hackers may attempt more serious data breaches behind the scenes.
Real-World Examples
To highlight the severity, consider the following high-profile cases:
- In 2016, attackers launched a major DDoS attack on Dyn, a DNS provider. As a result, websites like Twitter, Netflix, and Reddit went offline for hours.
- In 2023, several global banks experienced coordinated DDoS attacks that temporarily disrupted online banking services.
Clearly, no one is immune to this type of threat.
How to Protect Against DDoS Attacks
Although DDoS attacks are challenging, you can take proactive steps to reduce your risk:
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): Services like Cloudflare and Akamai distribute traffic, reducing the load on your main server.
- Invest in DDoS Protection Services: These tools can detect and neutralize suspicious traffic before it causes harm.
- Keep Systems Updated: Regular updates patch vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
- Monitor Traffic Patterns: Unusual spikes in traffic can indicate the early stages of an attack.
By implementing these strategies, you can strengthen your defense and minimize potential damage.
Final Thoughts
In summary, DDoS attacks are becoming more common, but understanding how they work and how to prevent them puts you ahead of the curve. As cyber threats evolve, staying informed and proactive is no longer optional—it’s essential.




Comments are closed